Human Skeletal Muscle Cells (SkMC)
Primary Human Skeletal Muscle Cells isolated from different skeletal muscles from adult single donors.
PromoCell uses the Bioz AI engine to display product citations. This content is currently blocked due to your cookie preferences.
- Product Description
- Additional Information
- Data & Figures
- Technical Library
- Reference Literature
- Downloads
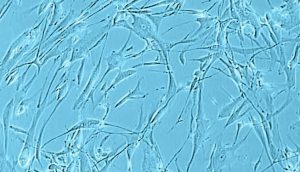
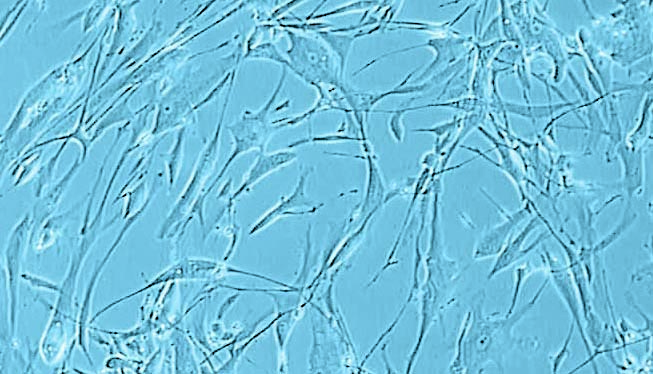
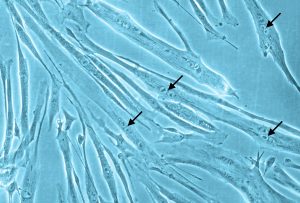
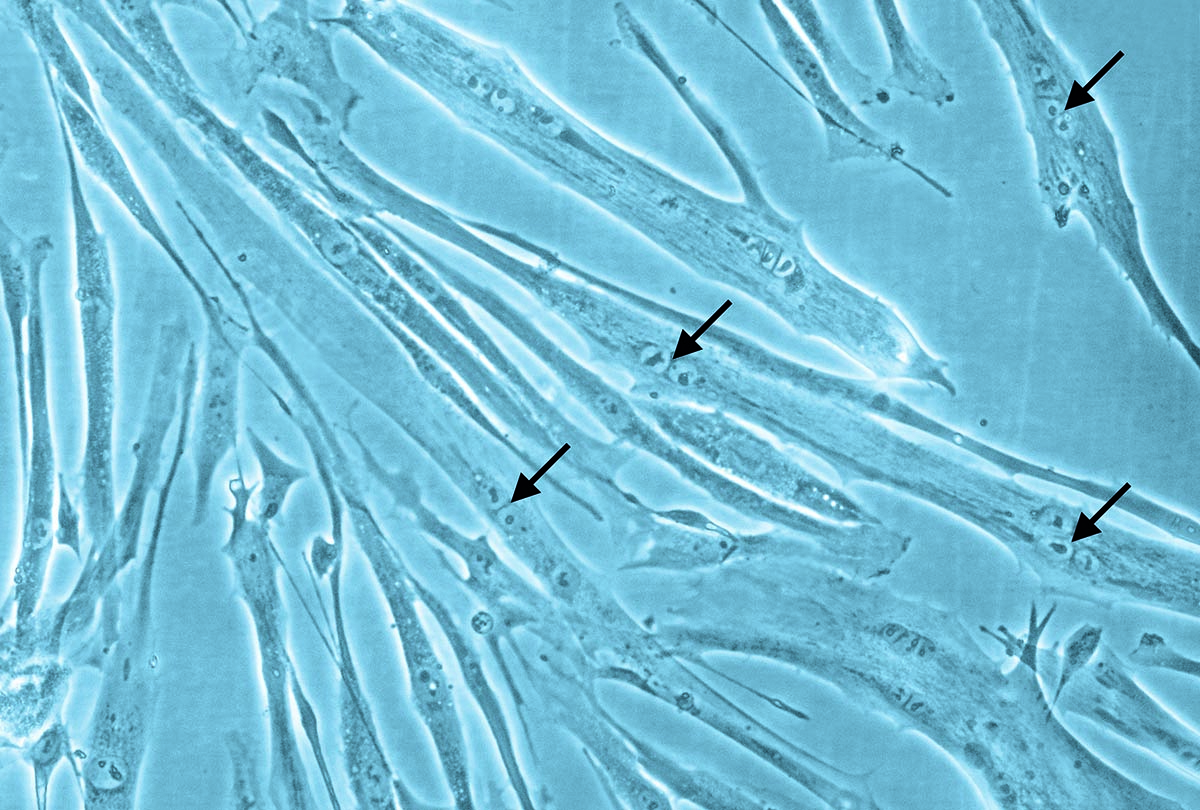
Primary Human Skeletal Muscle Cells (SkMC) are isolated from different skeletal muscles (e.g. Musculus pectoralis major) from adult single donors (lot specific source information is available on request).
New skeletal muscle cells originate from quiescent satellite cells, which are located in the muscle fibers between the basal lamina and the sarcolemma. Quiescent satellite cells are activated by stimuli such as muscle damage. After activation, the cells, now called myoblasts, start to proliferate and fuse with damaged muscle fibers or with one another forming new myotubes.
SkMC are optimal for in vitro muscle studies. They proliferate very well in the mitogen-rich Skeletal Muscle Cell Growth Medium. Fusion to myotubes with typical multinucleated syncytia can be induced by using the our Skeletal Muscle Cell Differentiation Medium.
NEW:
- Request our GMP compliant cell culture media for skeletal muscle cells.
- Our SkMC are now also available from HLA-typed donors.
Available formats:
- Cryopreserved: Cryogenic vial containing 500.000 viable cells.
- Proliferating: >500.000 viable cells shipped in growth medium (T25 flask).
- Cell pellet: 1 million cells dissolved in 200µl RNAlater© for subsequent RNA, DNA or protein analysis. Cell pellets cannot be revived.
| Recommended plating density | 3,500 – 7,000 cells per cm2 |
|---|---|
| Passage After Thawing | P2 |
| Tested Markers | Differentiation capacity to multinucleate syncytia tested |
| Guaranteed Population Doubling | > 15 |